Antilock Braking System (ABS) and Its Components: Enhancing Vehicle Safety
Stay in control on the roads with Antilock Braking System (ABS)! Discover how this cutting-edge technology and its components are revolutionizing vehicle safety.
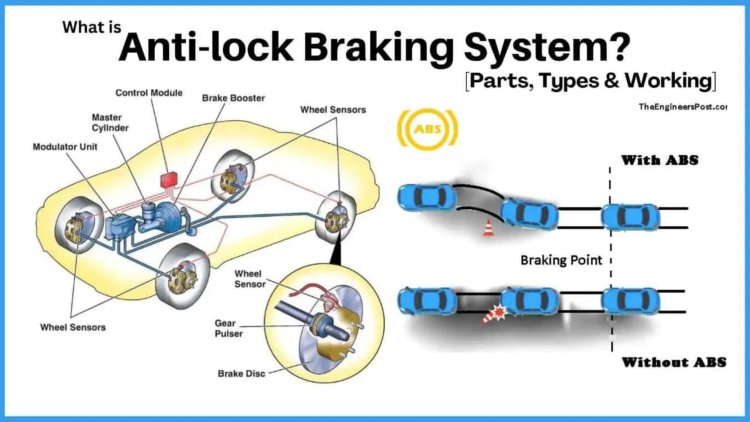
In the ever-evolving realm of automotive technology, safety remains a paramount concern. One crucial innovation that has significantly contributed to enhancing vehicle safety is the Antilock Braking System (ABS). ABS is an integral component of modern vehicles, offering improved control and preventing wheel lock-up during braking. In this article, we delve into the functioning and components of ABS, focusing on its significance in the Indian automotive landscape.
Suggested: Exploring the Pros and Cons of CNG, Hybrid, and Petrol Cars: Which One Is Right for You?
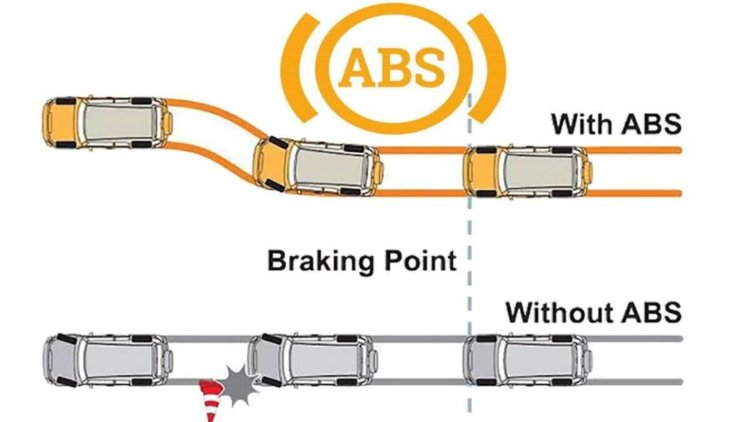
Functioning of ABS: The primary function of ABS is to prevent the wheels from locking up, thereby allowing the driver to maintain steering control during hard braking or on slippery surfaces. ABS achieves this through a sophisticated system of sensors, valves, and control units that work seamlessly together. When the driver applies the brakes firmly, the ABS sensors detect any potential wheel lock-up.
Components of ABS:-
1. Wheel Speed Sensors: ABS relies on wheel speed sensors to monitor the rotational speed of each wheel. These sensors provide real-time data to the ABS control unit, enabling it to determine if any wheel is at risk of locking up. In India, where diverse road conditions prevail, wheel speed sensors play a crucial role in ensuring optimal braking performance.
2. Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU): The HCU is the central control module of the ABS system. It receives signals from the wheel speed sensors and activates the ABS when necessary. The HCU is responsible for modulating brake fluid pressure to individual wheels, effectively preventing them from locking up. In the Indian context, where sudden stops and braking on uneven surfaces are common, the HCU plays a vital role in maintaining vehicle stability.
3. Pump and Valves: The ABS system incorporates a pump and valves that control the flow of brake fluid. When the ABS detects wheel lock-up, the valves quickly reduce brake fluid pressure on the affected wheel, allowing it to regain traction. This cyclic modulation of brake pressure ensures that the vehicle maintains optimal stability and minimizes the risk of skidding. The pump assists in maintaining adequate brake fluid pressure during ABS operation.
4. Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU acts as the brain of the ABS system, continuously monitoring wheel speed sensor inputs and making rapid calculations to determine the necessary adjustments to brake fluid pressure. It ensures that the ABS system engages only when required, optimizing brake performance and allowing the driver to maintain control. The ECU also communicates with other vehicle systems, such as the engine management system, for coordinated operation.
Suggested: Drive with peace of mind: Discover India's top 10 safest cars and their standout features
The Antilock Braking System (ABS) is a crucial safety feature in vehicles, particularly in India's diverse and challenging driving conditions. By preventing wheel lock-up during braking, ABS enables drivers to maintain control, reducing the risk of accidents. The various components of ABS, including wheel speed sensors, hydraulic control unit, pump and valves, and electronic control unit, work together harmoniously to provide effective anti-lock braking capabilities. As technology continues to advance, ABS systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, contributing to safer roads and improved vehicle safety across the country.